Flora
Profile
Institut Pertanian Bogor (IPB)
Flora Diversity
Based on the census method, the number of rare plants living in the cikabayan area is 141 trees consisting of 9 (nine) types of trees. The most common type of rare plant in the Cikabayan area is Rasamala (Liquidambar excelsa) plant as many as 37 trees. There are 7 (seven) families of rare plants living in the Cikabayan area. The largest family is in the Family Dipterocarpaceae with a total of 40 trees and at least the family Rutaceae with several 3 (three) trees.
Important Value Index (INP)
The highest Important Value Index (INP) value on United Tractors plants in IPB University area is Rasamala type (Liquidambar Excelsa) with INP 37.35%. While the lowest INP value in United Tractors plant in Cikabayan area is Sanrego type (Lunasia Amara) with INP 13.24%.The high value of INP Rasamala (Liquidambar excelsa) because it has a greater number of individuals compared to other types.
Biodiversity Status and Trends
Pantai Indah Kapuk (PIK)
General Condition of Pantai Indah Kapuk (PIK)
The observation location is not exactly in the coastal area, but it is still affected by the tides of the sea and at the beginning of planting (2010) the area is completely submerged, and it is difficult to do mangrove planting. So that at that time carried out planting with guludan technique. The region was stagnant ten years ago and the intensity was stagnant for a very long time, but now it has started to dry out even in the rainy season.
Important Value Index (INP)
The results of sampling plot measurements in the field that recorded plant species (mangrove plants) at the stake level with a diameter range from 5 cm to 9 cm and on average only 3 – 4 cm in diameter, growth tends to lead to height and slightly stretch with plants between clumps. The density value of 8,200 individuals per hectare (within an area of 10,000 m2). In factual calculation in the field with an area of planting area of 0.2 ha ( 2000 m2), the amount of diversity measured in sampling vegetation analysis at the stake level is 0.615. Besides, there are also types of ecotone plants and lowland forests around the planting area associated with the types of mangroves that are clustered as a whole.
At the tree level (diameter above 10 cm) there is measurable data in the form of natural plants or plants that have long existed before mangrove planting which is currently associated with existing mangrove plants. The sampling calculation was obtained a tree diversity value of 0.943 filled by ecotone plants and lowland forests as in the following table.
Biodiversity Status and Trends

Taman Kanal Banjir Timur (KBT)
General Condition of Taman Kanal Banjir Timur (KBT)
The area of BKT Park is 3.9 hectares with a length of 1.4 Km. The elongated park is separated by an alternative road. Based on the condition of this road, the study was made into several blocks, including block 1, block 2, block 3, and block 4. The topography in KBT Park has a flat contour with a maximum height of 21 meters above sea level. The slope in KBT Park ranges from 1-5%. The soil in KBT Park is sandy clay. This land is considered quite fertile and suitable for vegetation growth. The land will be inundated in the rainy season but KBT Park has an open parallel drainage system and has a channel length of 3-8 m and a depth of 20 cm located in the middle of the park. This drainage has major drainage in the north which results in the flow of water not directly into the canal but to the north side of the park.
Important Value Index (INP)
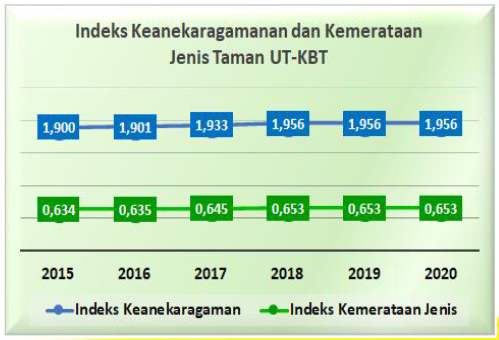
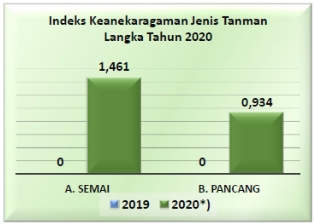
Biodiversity Status and Trends